'Method of fabricating composite electrodes for electrodeionization of water based by cross-linking graphene oxide' was awarded a silver medal at the 48th International Exhibition of Inventions in Geneva. The inventors behind it are a group of researchers from the TUL Institute of Materials Science and Engineering: dr hab. inż. Konrad Dybowski, TUL professor, Professor Łukasz Kaczmarek, Professor Piotr Kula, dr inż. Witold Szymański, Tomasz Warga, Grzegorz Romaniak, Bartosz Bucholc, Magdalena Makowicz, as well as Jan Siniarski and Tomasz Kaźmierczak from AMII Łódź.
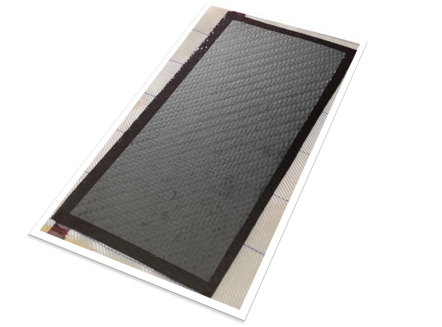
The subject of the invention is a graphene electrode for water electrodeionization processes. It is an electrode made of carbon fibers (epoxy bonded), coated with cross-linked reduced graphene oxide.
The process of fabricating the graphene electrode involves two key steps - activation of the surface of the carbon fibers and coating them with a layer of cross-linked graphene oxide.
The main advantage these carbon electrodes provide compared to the commercially available electrodes is their low cost with no durability loss. The electrodes display excellent electrical conductivity and high chemical and electrochemical resistance in aqueous environments of varying pH as well as low sensitivity to organic contaminants.
The graphene electrode facilitates rapid sorption and desorption of ions from water, including from solutions characterized by low electrical conductivity. Furthermore, due to the components used in the structure and the simple technology of fabrication, there are virtually no limitations on the size and shape. The solution affords a high degree of freedom in technological scalability.
The above described method of electrode fabrication was developed during the project No. POIR.04.01.04-00-0089/15, Measure 4.1 ‘Research and development', Sub-measure 4.1.4 'Application projects', called 'Graphene composite materials for water purification', conducted by the consortium of Lodz University of Technology (leader) and Amii Sp. z o.o.
The invention has been patented: Patent No: 236678.